
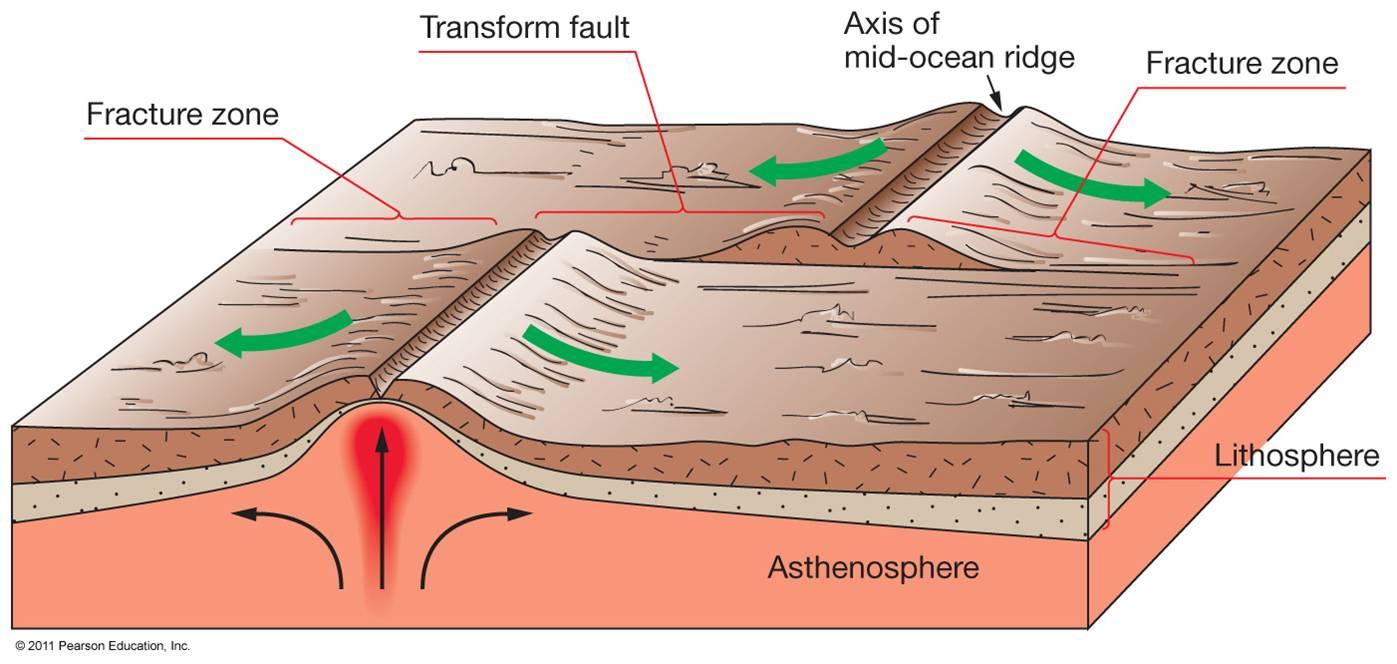
Transform Fault A transform fault marks a conservative plate margin, i.e. Examples include the Lizard Thrust in Cornwall and the Moine Thrust in Scotland. They are often found near convergent (destructive) plate margins, but may occur some distance from them. Thrusts indicate horizontal shortening by compression. Thrust FaultA reverse fault at an angle of less than 45 (but generally at a much shallower angle). Tethys Ocean The ocean that opened between the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia during the breakup of Pangea. The Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland, and the geology of eastern Greenland, are clear evidence for this event. Tertiary Volcanic Province An area of extensive basaltic volcanism in the north west of the UK which marked the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean approximately 57 million years ago. At depth, the subduction zone is marked by earthquakes, some of which are deeper than 400 km. At the surface the subduction zone generally coincides with the bottom of oceanic trenches. Subduction Zone A zone where oceanic lithosphere is recycled back into the mantle. As magmas rise up, they mimic the same process, exploiting weaknesses such as joints, bedding planes and faults, breaking off blocks of the country rock that then fall through the rising magma onto the floor of the magma chamber. Stoping Stoping is a mining term used to describe the removal of overlying roof rock so that it falls to the floor of a mine.

It is believed to be the major force driving plate motions. As a result of its own weight, the descending plate is pulled by gravity through the mantle asthenosphere, which is hotter and less rigid. At a convergent plate boundary the oceanic lithosphere sinks beneath the adjacent plate forming an ocean trench and subduction zone. Slab Pull As oceanic lithosphere cools, it becomes denser and thicker. First proposed by Harry Hess following echo sounding work to reveal the topography of the ocean basins. Radiometric dating and fossil evidence shows that the sea floor becomes progressively older in both directions away from mid ocean ridges. New oceanic crust is formed as two oceanic plates move apart. The continental plate is pushed upward creating mountains like the Andes.Sea Floor Spreading The process by which oceans are formed at divergent (constructive) plate margins.
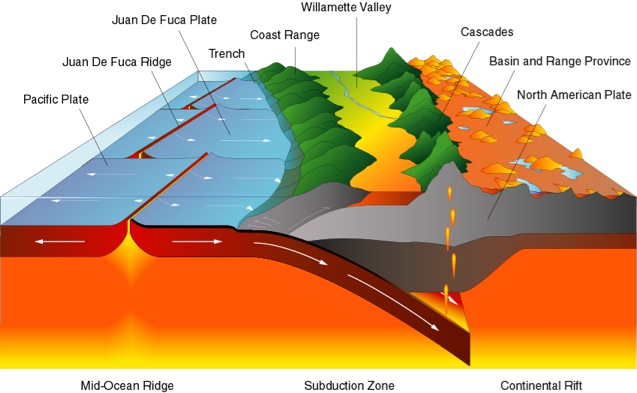
As the Ocean plate is pushed under the continental plate the sedimentary layers are melted creating volcanos. The resulting subduction zone creates a deep ocean trench and mountains. An example is the Pacific Coast of South America. The most common convergent boundary is where an ocean plate is being pushed under a continental plate. An example is the rift valley of East Africa.Ĭonvergent boundaries occur where two plates are being pushed together. Examples are the mid ocean ridges and Icelandic volcanoes.Īlso because the plates are moving in opposite directions new crust is formed between the two plates. These boundaries produce shield type volcanos that spew out ballistic lava. This pushing creates frequent and severe earthquakes, like the famous San Francisco earthquake.ĭivergent boundaries occur where two plates are being pushed apart as new crust and magma comes to the surface. Transform faults occur where two plates are pushing against each other at a close to a 180 degree angle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
